Accounting equation
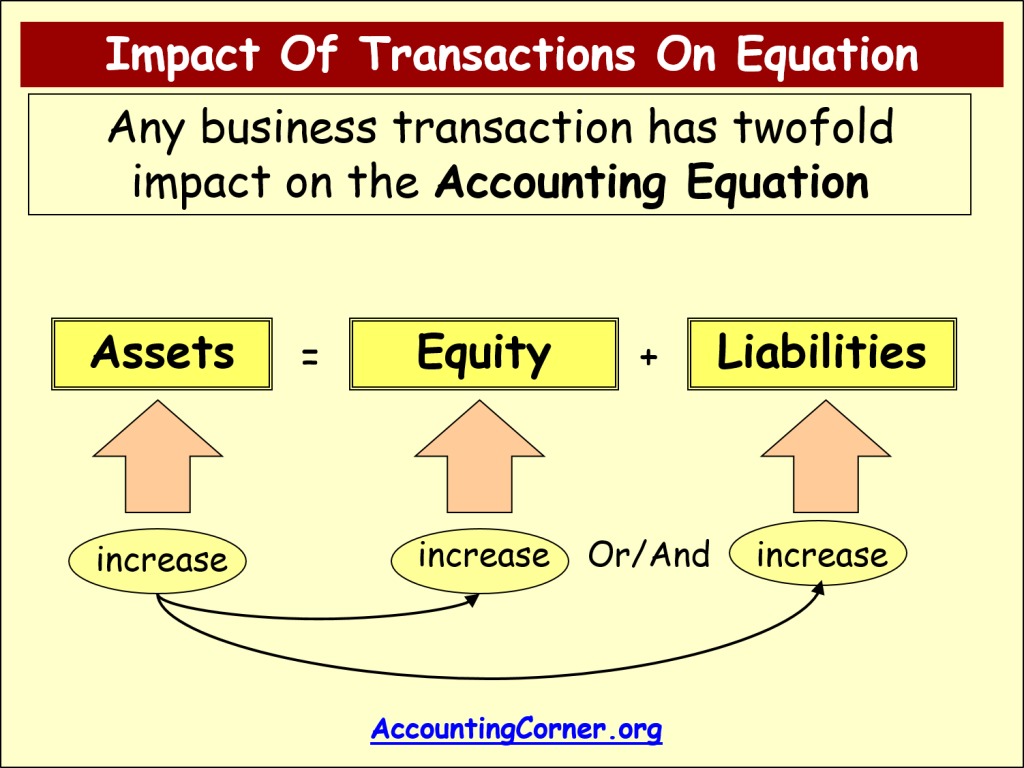
The fundamental accounting equation, also called the balance sheet equation, is the foundation for the double-entry bookkeeping system and the cornerstone of accounting science. Like any equation, each side will always be equal. In the accounting equation, every transaction will have a debit and credit entry, and the total debits (left side) will equal the total credits (right side). In other words, the accounting equation will always be “in balance”.
Financial statements
A company’s quarterly and annual reports are basically derived directly from the accounting equations used in bookkeeping practices. These equations, entered in a business’s general ledger, will provide the material that eventually makes up the foundation of a business’s financial statements. This includes expense reports, cash flow and salary and company investments.
Double entry bookkeeping system
The accounting equation plays a significant role as the foundation of the double-entry bookkeeping system. The primary aim of the double-entry system is to keep track of debits and credits and ensure that the sum of these always matches up to the company assets, a calculation carried out by the accounting equation. It is based on the idea that each transaction has an equal effect. It is used to transfer totals from books of prime entry into the nominal ledger. Every transaction is recorded twice so that the debit is balanced by a credit.
Income and retained earnings
The income and retained earnings of the accounting equation is also an essential component in computing, understanding, and analyzing a firm’s income statement. This statement reflects profits and losses that are themselves determined by the calculations that make up the basic accounting equation. In other words, this equation allows businesses to determine revenue as well as prepare a statement of retained earnings. This then allows them to predict future profit trends and adjust business practices accordingly. Thus, the accounting equation is an essential step in determining company profitability.
Company worth
Since the balance sheet is founded on the principles of the accounting equation, this equation can also be said to be responsible for estimating the net worth of an entire company. The fundamental components of the accounting equation include the calculation of both company holdings and company debts; thus, it allows owners to gauge the total value of a firm’s assets.
However, because accounting is kept on a historical basis, the equity is typically not the net worth of the organization. Often, a company may depreciate capital assets in 5–7 years, meaning that the assets will show on the books as less than their “real” value, or what they would be worth on the secondary market.
Investments
Due to its role in determining a firm’s net worth, the accounting equation is an important tool for investors looking to measure a company’s holdings and debts at any particular time, and frequent calculations can indicate how steady or erratic a business’s financial dealings might be. This provides valuable information to creditors or banks that might be considering a loan application or investment in the company.[6]
Double-entry bookkeeping
Introduction
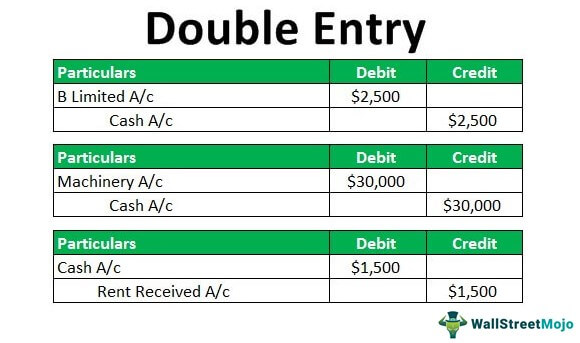
Double-entry accounting refers to the method of bookkeeping which helps a company to maintain its account and keep it balanced which shows the true picture of the finances of the company. Double-entry refers to the use of an accounting asset which is a summation of liabilities and equity. The credits of an account should be equal to keep an equation in perfect balance. Accountants make use of the credit and debit entries so that they can record the transactions of all the accounts. All these credits and debits are shown in the Balance Sheet.
Types of Accounts
All the day to day finally activities are recorded and measured by the accounting and bookkeeping process. An event between two economic entities like between customer and business, or vendor and business-like known as a transaction. To record this event we use accounting and bookkeeping.
A systematic accounting process is a procedure under which the activities of the business are recorded under systematic accounts to keep data sorted and classified under different heads.
To classify all the business accounting entries and transactions there are 7 main types of accounts, which are :
- Assets
- Liabilities
- Equity
- Gains
- Losses
- Expenses
- Revenues
The continuous process of tracking changes in various types of accounts while continued business operations are known as accounting and book-keeping.
Double Account System
The meaning of the double-entry system is generally based on the Dual Aspect Concept. The Dual Aspect Concept is based on the fundamentals of accounting principles. All the transactions related to the business are recorded in the book which is specifically based on the principle of accounting.
According to the Dual Aspect Concept, all business transactions have a two-way or dual effect. This tells us that the business transaction of the particular entity has a minimum of two accounts which are recorded in the books. This principle is known as the double-entry concept or system.
Single Entry System Meaning
A single entry system refers to the form of bookkeeping where each company maintains its financial transactions in a single-entry log. The single-entry system does not involve any formal training and is usually based on new businesses because of its cost-effectiveness and simplicity.
The single entry system records the description, date, transaction value, expenses and income, and lastly balance. This is maintained while doing every transaction for the company. It also includes income tax depending on the type of business.
Who Uses A Single Entry System?
Small businesses use a single entry system. They record bare essentials only and the criteria for a company to be rendered fit for such a system are:
- Having few employees.
- Ones that use transactions based on cash
- Very fewer transactions
- Do not have an installment plan
- Have fewer physical assets like equipment, buildings, and vehicles
Single Entry System and Double Entry System
There are a few significant differences between the single entry system and the double-entry system. These are:
- The single entry system tells about debtors, cash, and creditors’ cash balance only whereas the double-entry system tells about all the business entities
- The records in the single entry system are only related to business. The records in the double-entry system affect all the transactions in the business.
- The single entry system has an incomplete way of maintaining transactions. In a double-entry system, it is difficult to carry out fraud.
- Errors cannot be easily found in a single entry system while errors can be easily detected in a double-entry system.
- The single entry system is not accepted by the tax department but the double-entry system is accepted by the taxation department.